What are GANs?
Unlike previous deep learning fields which focus on classifying things, generative models try to produce things. Classifying an image as drawn by Monet or as a fake is easy, but creating a drawing in the Monet style is quite challenging. GANs are the solution to this challenge. Cool, isn’t it?
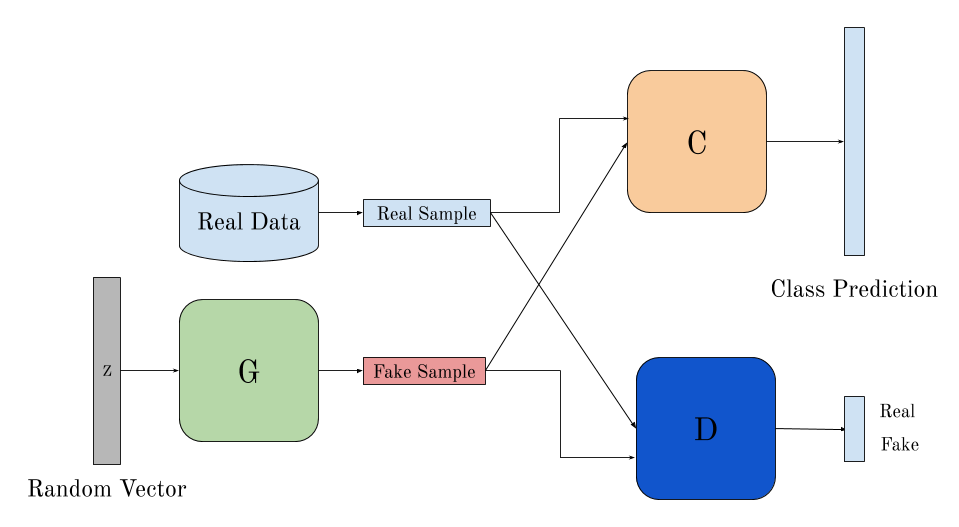
Generator And Discriminator
GANs try to achieve what they promise to do by using an adverserial process of training two networks simultaneously ,the Generator network which tries to capture the data distribution by producing stuff from absolute noise, and the Discrimnator network which tries to tell the probability that the data point came from the original distribution compared to the generator network. This turns out to be a MiniMax two player game.
Adverserial Nets
Both the networks are multilayer perceptrons. G(z;θg) is a differentiable function such that z is sampled from random noise and θg are the parameters we wish to learn. D(x;θd) is the second network that takes x either from the generator netowrk or the original distribution and predicts the probability of its coming from the latter to its former.
D is trained so as to maximise the assigning of correct labels to data from original distribution and that from G. Simultaneously G is trained to fool D. Mathematically , the attempt is tominimize log(1 – D(G(z))).
Essentially it boils down to a two player MiniMax Game with value function V(G,D). minGmaxDV(D,G) =Ex∼pdata(x)[logD(x)] +Ez∼pz(z)[log(1−D(G(z)))]
The Training Process The following Algorithm is generally followed to train the network.
- Sample a minibatch of m samples from training data set and m samples from the noise distribution.
- Update the discriminator by ascending its stochastic gradient.
∇θd1mm∑i=1[logD(x(i))+ log(1−D(G(z(i))))]
- Sample a minibatch of m samples from the noise distribution.
- Update the generator by ascending its stochastic gradient.
∇θg1mm∑i=1log(1−D(G(z(i))))
Wide Applications of GANs
So the big question is why should one learn about GANs? One impetus is definitely the cool applications it has. Listed below are some really amazing applications that would surely want you to explore more about GANs and want to try them out.
Creating Anime Characters Heavy tasks like game generation and animation will reduce much human labour with the advent of GANs. ![Image] (https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/14oqZHrOOZRDzMsJA_eqW1g.png) Text to Image We can input a sentence and generate multiple images fitting the description. ![Image] (https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/1okKk6wH36cuCbQJdmkP7ng.png) Face Aging An attempt to produce the probable images at differnet ages of an input image by trying to retain most of th salient features. ![Image] (https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/1*r4IQ7Z5fIm7ugpFnpfltYA.png)
References
Inspired enough? Check out the original research paper on GANs by Ian Goodfellow and begin rightaway! [Original Paper on GANs by Ian Goodfellow] (https://arxiv.org/pdf/1406.2661.pdf)